Learn how to create a development environment with a database server and a client. We will setup two docker containers running postgreSQL database and pgAdmin, the client web interface.
- Create a directory
postgresand inside it create a file with the name.env. This file will contain our credentials.
mkdir ~/postgres
touch .env
nano .env
- Store the following credentials in the
.envfile:
POSTGRES_USER=todoappusr
POSTGRES_PW=changeit
POSTGRES_DB=tododb
PGADMIN_MAIL=yourEmail@example.com
PGADMIN_PW=changeit
Start a Postgres DB server
- Go to the same directory,
postgresand create a file with the namedocker-compose.yml.
cd ~/postgres
nano docker-compose.yml
- This will be the Docker compose file for running two services, one for the postgreSQL database server and another service that runs the pgAdmin web interface. To start this simple setup, add the following to the
docker-compose.ymlfile.
services:
postgres:
container_name: postgres
image: postgres:15-alpine
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=${POSTGRES_USER}
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=${POSTGRES_PW}
- POSTGRES_DB=${POSTGRES_DB}
ports:
- "5432:5432"
restart: always
pgadmin:
container_name: pgadmin
image: dpage/pgadmin4:latest
environment:
- PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL=${PGADMIN_MAIL}
- PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD=${PGADMIN_PW}
ports:
- "5050:80"
restart: always
Notice that in the docker-compose.yml file we reference the environment variables defined in the .env file (e.g., POSTGRES_USER).
- Create and start the containers. Make sure that you’re inside the directory that contains the
docker-compose.ymlfile and run:
docker compose up
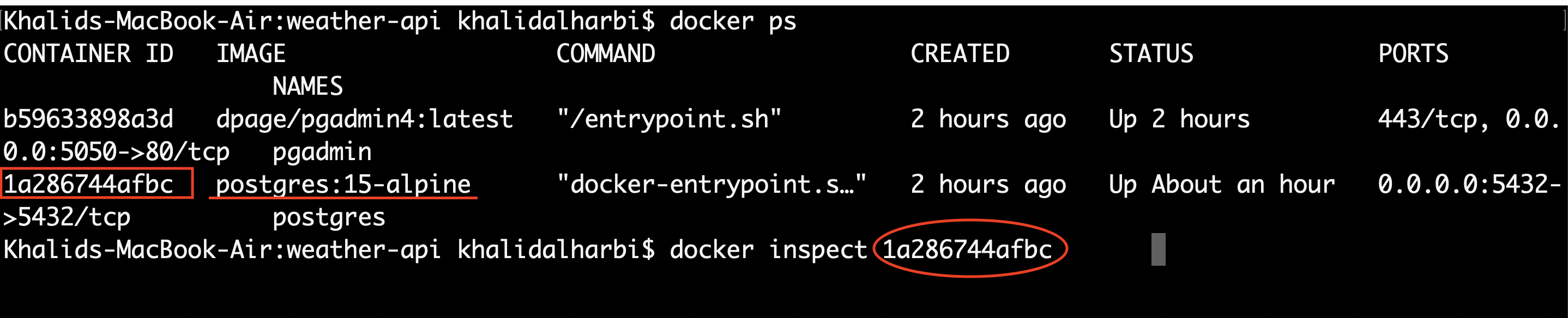
- Get the IP address of the container that runs Postgres.
docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
b59633898a3d dpage/pgadmin4:latest "/entrypoint.sh" About an hour ago Up About an hour 443/tcp, 0.0.0.0:5050->80/tcp pgadmin
1a286744afbc postgres:15-alpine "docker-entrypoint.s…" 2 hours ago Up About an hour 0.0.0.0:5432->5432/tcp postgres
- Run
docker inspect <container_id>. In our example, it’s:
docker inspect 1a286744afbc
...
],
"NetworkID": "41a86ebbf14e0fd0b613d2088c8d908b096094660939e06188519d636f1acde4",
"EndpointID": "a26af6d2c3c24aa8ca8b6e84652444188048bfb9b1ab997374e213573e243fa3",
"Gateway": "172.19.0.1",
"IPAddress": "172.19.0.3",
"IPPrefixLen": 16,
"IPv6Gateway": "",
"GlobalIPv6Address": "",
"GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:13:00:03",
"DriverOpts": null
}
- Copy the value of the “IPAddress” of the container that is running Postgres (in our example, the container’s image is postgres:15-alpine and the id is 1a286744afbc)
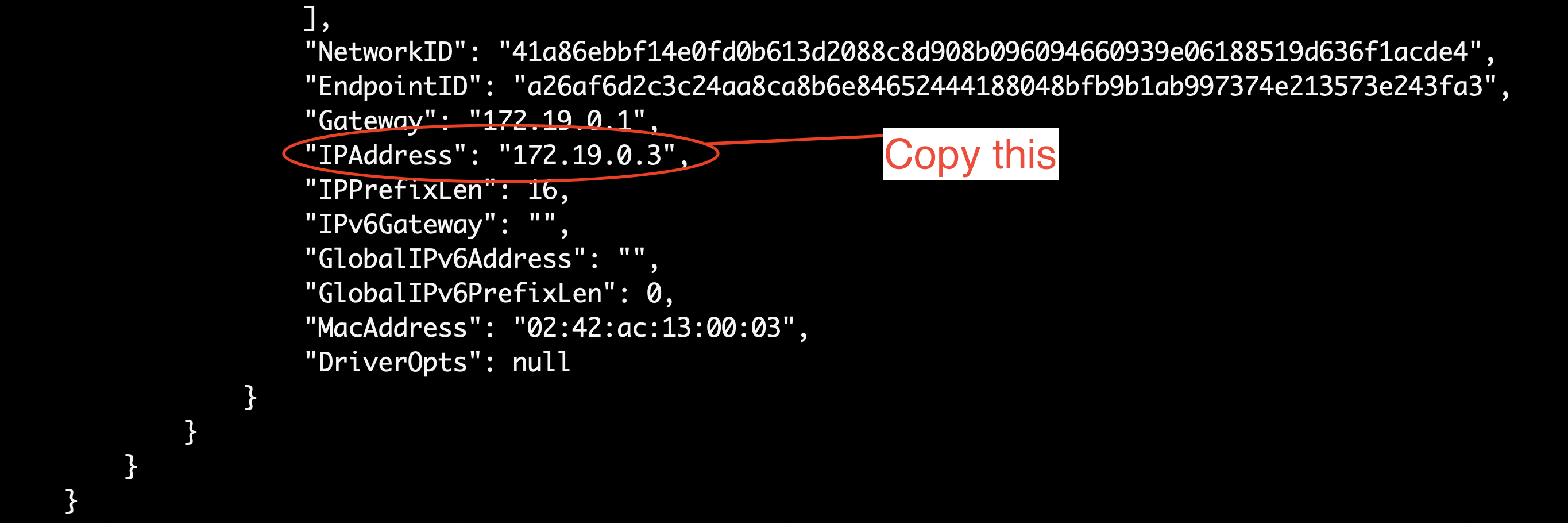
- In the following steps, we will use this IP address of the container that’s running the Postgres server to connect to the database server.
connecting to the database server
- Open your browser and go to: =http://localhost:5050
- log into pgAdmin using the credentials (email and password) defined in the
.envfile.
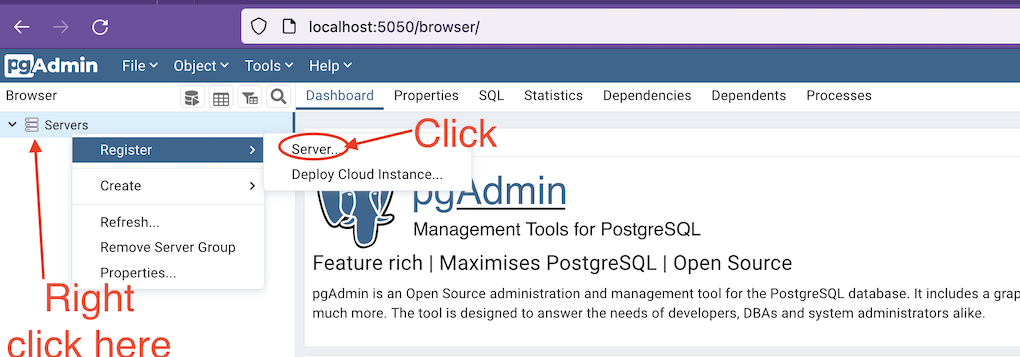
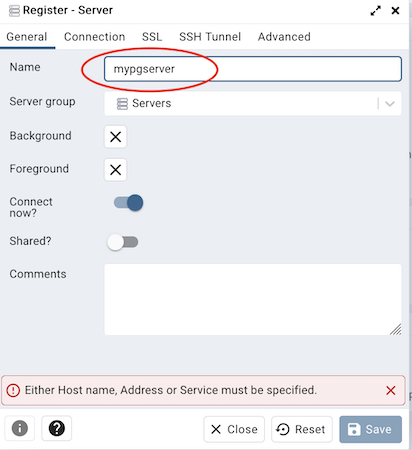
- On the top left pane, right click on “Servers” and select “Register” -> “Server”
- On the General tab, enter a name (e.g., mypgserver)
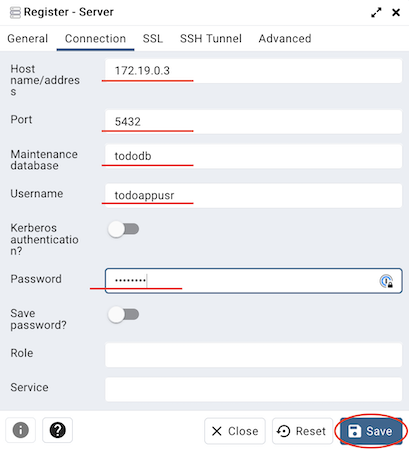
- Click on the “Connection” tab and enter the following:
- Host: <container’s_ip_address>
- 5432
- Email: get it from the
.envfile. - Password: defined the
.envfile.
Setting up the database
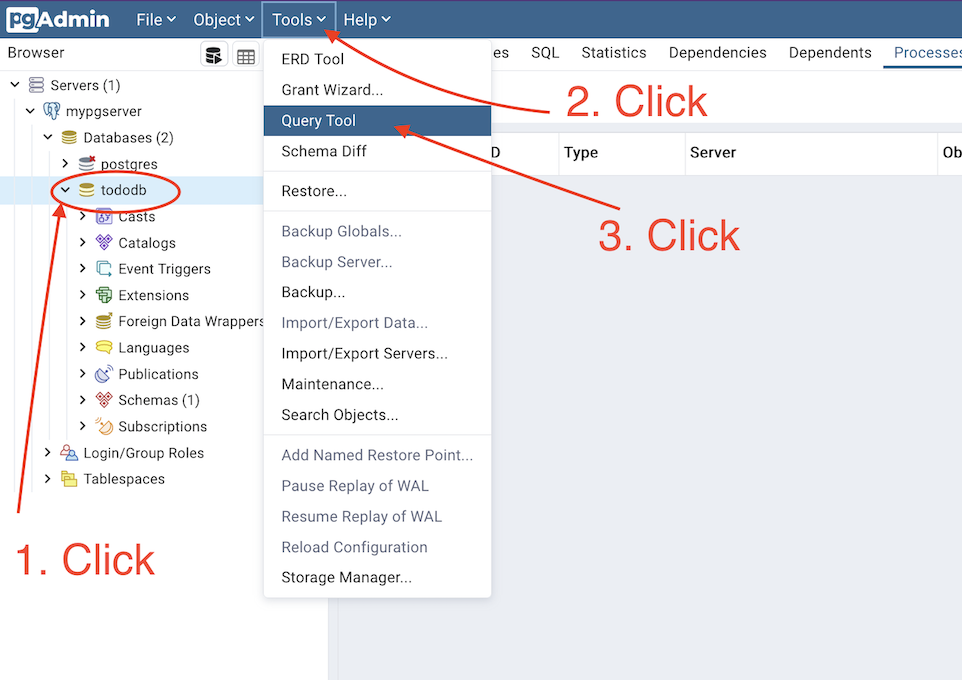
- From the top left pane, expand “Servers” -> “Databases” -> “tododb”.
- Click on the “Tools” menu and select “Query Tool”.
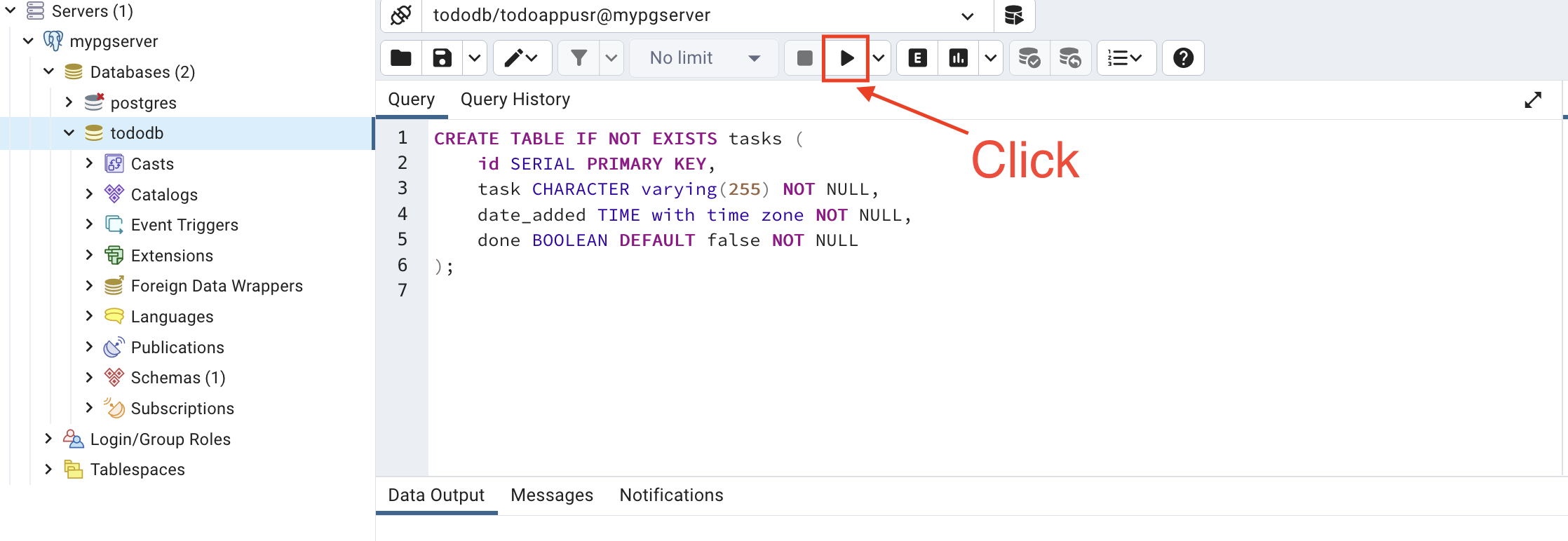
- Copy and paste the following SQL code to create the database table.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
task CHARACTER varying(255) NOT NULL,
date_added TIME with time zone NOT NULL,
done BOOLEAN DEFAULT false NOT NULL
);
In-class Activity
Install Docker on your local machine or a VM instance and follow the steps above to setup a Postgres environment and dockerize a web app written in PHP that uses this database. The PHP app can be found at gitlab.com/cpit490/php-postgres-todo-app. Submit a PDF file that contains screenshots of your screen as you work on this task.