In this lecture note, we will deploy a sample Java function for IP geocoding (determining the geographic location of an IP address) to demonstrate the use of Java in Azure Functions. The function will be HTTP-triggered, tested locally, and then deployed to serverless Azure Functions.
Introduction
We’ll create a serverless function that accepts an IPv4 address as input and returns the country code. The function will use an open dataset that provides geolocation data for IPv4 addresses worldwide.
Please note that the accuracy of this dataset is limited, and it should not be used in a production environment. For more reliable results, consider using the MaxMind GeoIP2 database, which requires an access key.
Prerequisites
- Install the Azure CLI
- Windows: Download and run the Azure CLI from here
- macOS: Use Homebrew to install the Core Tools on macOS using
brew update && brew install azure-cli - Linux: use your package manager (e.g., APT) to install it as described here
- Install Apache Maven
- Windows
- Visit the Maven download page and download the binary zip archive of the latest version of Maven (e.g.,
apache-maven-<version>-bin.zip). - Extract/unzip it to a new directory (e.g.,
C:\Program Files\Maven\). - Open the Start menu and search for environment variables.
- click on Edit the system environment variables.
- Under the Advanced tab in the System Properties window, click Environment Variables.
- Click the New… button under the System variables section to add a new system environment variable.
- Enter MAVEN_HOME as the variable name and the path to the Maven installation directory as the variable value. Click OK.
- Under the System variables section, click on Path to select it and click the Edit… button.
- Click the New button in the Edit environment variable window.
- Enter
%MAVEN_HOME%\binin the new field. Click OK to save changes to the Path variable. Click OK - Close and open PowerShell, and run
mvn -versionto confirm that you have maven installed successfully.
- Visit the Maven download page and download the binary zip archive of the latest version of Maven (e.g.,
- macOS
- Install Homebrew if you do not already have it.
brew install maven
- Linux
- Use your package manager (e.g.,
apt install maven)
- Use your package manager (e.g.,
- Windows
- The Java Development Kit (JDK) 21.
- You must set the set the
JAVA_HOMEenvironment variable. For more information, see this tutorial on how to set JAVA_HOME - Sign in into Azure CLI
- Close and reopen any active terminal window and run:
az login- When you sign in, Azure CLI generates and stores an authentication refresh token, which is used to obtain a new access token when the current one expires:
az account get-access-token
- Close and reopen any active terminal window and run:
Deploying an Azure Function in Java using Visual Studio Code
We will create and deploy the Java function code to Azure using Visual Studio Code.
Open Visual Studio Code, from the View menu, click Extensions or use the keyboard shortcut
Ctrl+Shift+X(Windows/Linux) orShift+Command+X(macOS), and install the following extensions published by Microsoft:Sign in to Azure in VS Code
- In Visual Studio Code, in the Activity bar, select the Azure icon. Then under Resources, select Sign in to Azure.
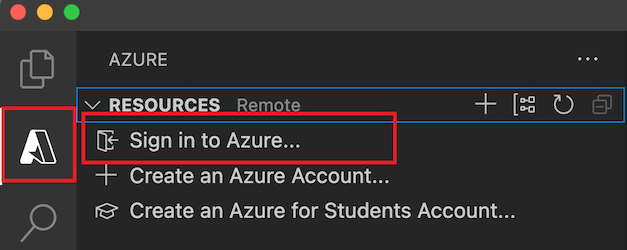
- In Visual Studio Code, in the Activity bar, select the Azure icon. Then under Resources, select Sign in to Azure.
Create an Azure Function App at Azure Portal
- In the Azure Portal, search for Function App and click on it
- Click + Create
- From the hosting options, select Flex Consumption plan and click Select.
- Under Basics:
- Subscription: Select your subscription and Resource Group
- Function App name: Choose a globally unique name (e.g.,
GeoByIPFunc-YOURNAME) - Region: Select any supported region (e.g.,
eastus) - Runtime stack:
Java - Version:
21 - Instance Size: Select
512 MBor similar for the amount of memory needs to be allocated to each instance of the function app. - Zone redundancy: select
Disabled
- Under Networking: Make sure that Enable public access is turned On, and virtual network integration is Off.
- Under Monitoring: you may disable Application Insights.
- Under Resource authentication make sure that the selected Authentication type is Secrets
- Click Review + create then Create
- Once your deployment is complete, click on Go to resource.
Create the Function in VS Code
- Open a new Visual Studio Code window, press
F1on Windows orCommand+SHIFT+Pon macOS and search for and run the commandAzure Functions: Create New Project....
Prompt Selection Select the directory location for storing your project workspace Create a new empty directory (e.g., GeoByIPFunc) and choose it as the desired project directorySelect a language JavaSelect a version of Java Java 21Enter a Maven group id sa.edu.kau.fcit.cpit490Enter a Maven artifact id GeoByIPFuncEnter a Maven release version 1.0-SNAPSHOTEnter a Java package name sa.edu.kau.fcit.cpit490Enter the globally unique name for the App Name GeoByIPFunc-YOURNAMESelect build type MavenHow would you like to open your project? Open in current window - Open a new Visual Studio Code window, press
Write the Function Code
- We will use a CSV file that contains a list of IPv4 address ranges and the country code. This CSV file is part of this GitHub repository sapics/ip-location-db project.
- Open a Terminal window on VS Code (Terminal menu -> New Terminal) and download and move the
asn-country-ipv4-num.csvfile that contains the IPv4 address range and country codes:
curl -LO https://github.com/sapics/ip-location-db/raw/refs/heads/main/asn-country/asn-country-ipv4-num.csv
mkdir -p src/main/resources
mv asn-country-ipv4-num.csv src/main/resources/
- We will use a CSV parsing library as a dependency for our Maven project. Open the
pom.xmlfile in VS code and add the following to yourpom.xmlfile under the<dependencies>tag:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-csv</artifactId>
<version>1.14.1</version>
</dependency>
- With the
pom.xmlfile open, expand the left sidebar, select Maven, and click on the dual arrow icon to refresh the dependencies as shown below:
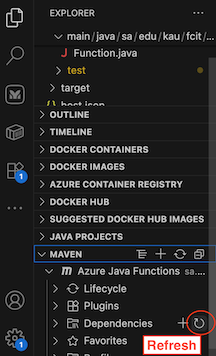
- Open the class
Function.java, which is typically atsrc/main/java/sa/edu/kau/fcit/cpit490/Function.javaand replace the code with:
package sa.edu.kau.fcit.cpit490;
import com.microsoft.azure.functions.ExecutionContext;
import com.microsoft.azure.functions.HttpMethod;
import com.microsoft.azure.functions.HttpRequestMessage;
import com.microsoft.azure.functions.HttpResponseMessage;
import com.microsoft.azure.functions.HttpStatus;
import com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation.AuthorizationLevel;
import com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation.FunctionName;
import com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation.HttpTrigger;
import org.apache.commons.csv.CSVFormat;
import org.apache.commons.csv.CSVParser;
import org.apache.commons.csv.CSVRecord;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Azure Functions with HTTP Trigger.
*/
public class Function {
/**
* This function listens at endpoint "/api/getLocation". To invoke it using
* "curl" command in bash:
* curl "{your host}/api/getLocation?ip=IPv4_ADDRESS"
*/
@FunctionName("getLocation")
public HttpResponseMessage run(
@HttpTrigger(name = "req", methods = {
HttpMethod.GET }, authLevel = AuthorizationLevel.FUNCTION) HttpRequestMessage<Optional<String>> request,
final ExecutionContext context) {
context.getLogger().info("Java HTTP trigger processed a request.");
// Get the IPv4 address as a query parameter
final String ipAddress = request.getQueryParameters().get("ip");
if (ipAddress == null) {
context.getLogger().warning("Java HTTP trigger processed a request.");
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
.body("Please provide an IP address using the 'ip' query parameter")
.build();
} else {
try {
String countryCode = getCountryFromIP(ipAddress, context);
if (countryCode != null) {
Map<String, String> responseData = new HashMap<>();
responseData.put("ip", ipAddress);
responseData.put("countryCode", countryCode);
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.OK).body(responseData).build();
} else {
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
.body("Country not found for IP: " + ipAddress)
.build();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
context.getLogger().severe("Failed to find country for IP: " + e.getMessage());
return request.createResponseBuilder(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body("Failed to find country for IP: " + e.getMessage())
.build();
}
}
}
/**
* Gets country code for an IPv4 address
*
* @param ipAddress The IPv4 address to look up
* @return The two-letter country code or null if not found
*/
public String getCountryFromIP(String ipAddress, ExecutionContext context) {
try {
long ipLong = ipToLong(ipAddress);
return lookupCountryCode(ipLong, context);
} catch (Exception e) {
context.getLogger().warning("Error looking up IP: " + e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
/**
* Converts an IPv4 address to a long integer for range comparison
*
* @param ipAddress The IPv4 address in string format (e.g., "192.168.1.1")
* @return The IP address as a long integer
* @throws UnknownHostException if the IP address is invalid
*/
public long ipToLong(String ipAddress) throws UnknownHostException {
String[] parts = ipAddress.split("\\.");
if (parts.length != 4) {
throw new UnknownHostException("Invalid IPv4 format: " + ipAddress);
}
InetAddress inet = InetAddress.getByName(ipAddress);
byte[] addressBytes = inet.getAddress();
if (addressBytes.length != 4) {
throw new UnknownHostException("Not an IPv4 address");
}
long result = 0;
for (byte b : addressBytes) {
result = (result << 8) | (b & 0xFF);
}
return result;
}
/**
* Looks up the country code for an IP address using the CSV dataset
* Note: The dataset file "asn-country-ipv4-num.csv" should be placed in the
* resources folder src/main/resources/
* and have the format: start_ip,end_ip,country_code
*
* @param ipLong The IP address converted to a long integer
* @param context The Azure Functions execution context for logging
* @return The two-letter country code or null if not found
*/
public String lookupCountryCode(long ipLong, ExecutionContext context) {
try {
InputStream is = getResourceAsStream("asn-country-ipv4-num.csv");
if (is == null) {
context.getLogger().severe("Error reading CSV file: resource not found");
return null;
}
try (InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(is, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
CSVParser csvParser = CSVFormat.DEFAULT.builder().get().parse(reader)) {
for (CSVRecord record : csvParser) {
if (record.size() < 3)
continue;
long startRange = Long.parseLong(record.get(0));
long endRange = Long.parseLong(record.get(1));
if (ipLong >= startRange && ipLong <= endRange) {
return record.get(2);
}
}
return null;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
context.getLogger().severe("Error reading CSV file: " + e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
/**
* Gets resource as stream - method made accessible for testing
*
* @param resourceName The name of the resource
* @return InputStream of the resource or null if not found
*/
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resourceName) {
return getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(resourceName);
}
}
- Next, we need to remove configuration settings that are not compatible with Azure Functions running on Flex consumption plan. Open
local.settings.jsonand replace the content with:
{
"IsEncrypted": false,
"Values": {
"AzureWebJobsStorage": "",
"FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME": "java"
}
}
Note: This file should never be checked into your git repository. Make sure it’s added to your
.gitignore.- Make sure that
java --versionreturns version 21. If it doesn’t, go back to the prerequisite section above, install JDK 21, and setJAVA_HOMEto point to the installation directory. - We also need to make changes to the
pom.xmland configure our Azure Function to use the Flex consumption plan with the required settings. Open thepom.xmland update the Azure Functions Maven plugin configuration namedazure-functions-maven-pluginas follows:
<plugin>
<groupId>com.microsoft.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-functions-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${azure.functions.maven.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<appName>${functionAppName}</appName>
<resourceGroup>java-functions-group</resourceGroup>
<!-- function app region-->
<!-- refers
https://github.com/microsoft/azure-maven-plugins/wiki/Azure-Functions:-Configuration-Details#supported-regions
for all valid values -->
<region>eastus</region>
<appServicePlanName>java-functions-app-service-plan</appServicePlanName>
<!-- Add Flex consumption pricing tier -->
<pricingTier>Flex Consumption</pricingTier>
<!-- Set minimum instances for Flex -->
<maximumInstances>40</maximumInstances>
<runtime>
<!-- Explicitly set OS to linux -->
<os>linux</os>
<javaVersion>21</javaVersion>
</runtime>
</configuration>
</plugin>
Please make sure that the region in
<region>eastus</region>matches your selected region.Add the following two test files FunctionTest.java and HttpResponseMessageMock.java under
src/test/java/sa/edu/kau/fcit/cpit490/.For the complete source code, please see the project repository at gitlab.com/cpit490/GeoByIPFunc.
- Start the function Locally
- You can start the function locally using one of the following options:
- Option 1: Using the VS Code Terminal. Terminal -> New Terminal and run
mvn clean package mvn azure-functions:run - Option 2: Using the VS Code Maven and Azure Functions extensions
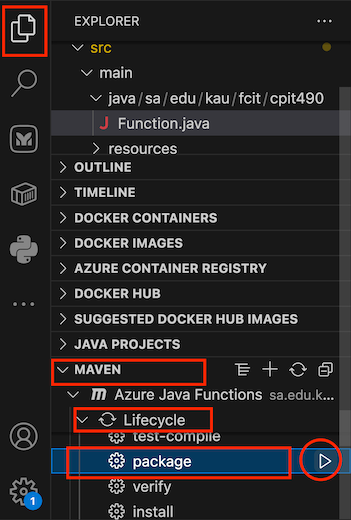
- From the left-hand side Activity bar, open the project explorer, select Maven -> Lifecycle -> Package as shown below:
- Open the Command Palette (For Windows Ctrl+Shift+P and macOS ⇧⌘P) and type:
Tasks: Run Taskand then selectfunc: host start
- From the left-hand side Activity bar, open the project explorer, select Maven -> Lifecycle -> Package as shown below:
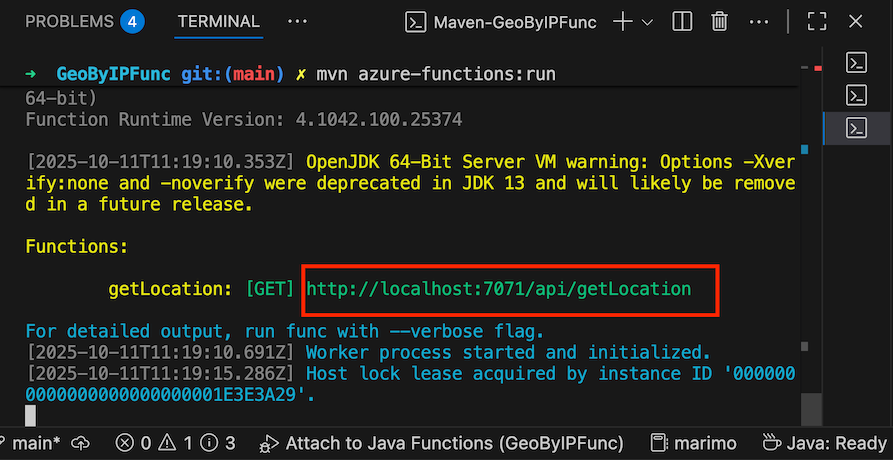
- The function should be running at
http://localhost:7071/api/getLocation. Copy this URL.Note: Please note that any changes made to the source code will require re-packaging the Maven project and re-running the function.
- Option 1: Using the VS Code Terminal. Terminal -> New Terminal and run
- Test the function locally
- Find your public IP address by either going to a website such as https://whatismyipaddress.com/ or running
curl https://ipinfo.io/ip - Test the function using:
- Find your public IP address by either going to a website such as https://whatismyipaddress.com/ or running
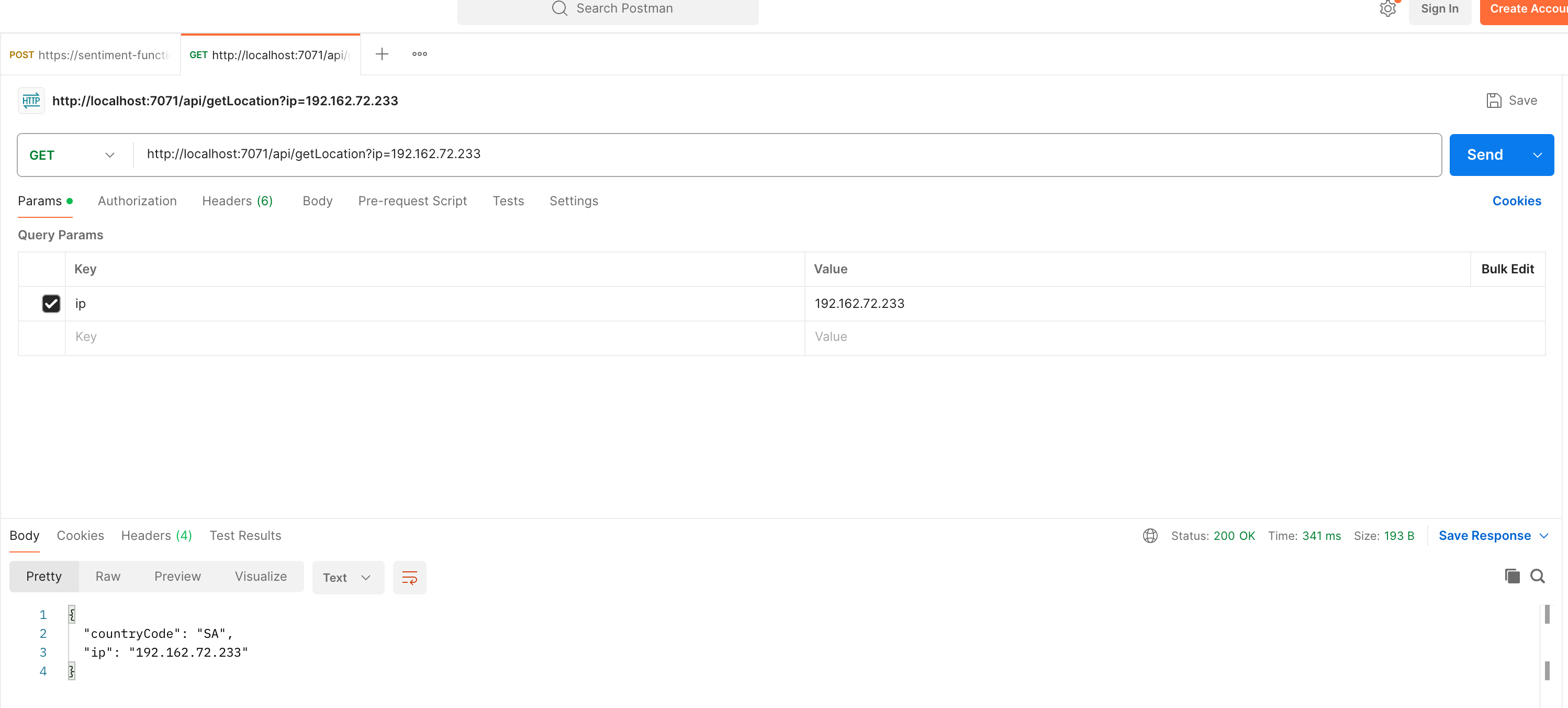
curl "http://localhost:7071/api/getLocation?ip=192.162.72.233"
{
"countryCode": "SA",
"ip": "192.162.72.233"
}
- You may also test the function using Postman:
- Publish the Function to Azure We will deploy the function project files directly to our Azure function app using zip deployment.
Stop the function that you ran locally using
CTRL-C.We will deploy the project files from the current directory to the
<FunctionAppName>as a .zip deployment package. Deployment can be done using either the Azure Functions Core Tools or the Azure Functions VS Code Extension.Option 1: Using Azure Functions Core Tools In the following command, replace
<FunctionAppName>with the name you chose on Azure in step 3 (e.g.,GeoByIPFunc-YOURNAME):
func azure functionapp publish <FunctionAppName>
- This should result in a successful deployment:
[2025-10-16T13:36:16.018Z] The deployment was successful!
Functions in geobyipfunc-cpit490:
- Option 2: Using VS Code Azure Functions Extensions
- Open the Command Palette (For Windows Ctrl+Shift+P and macOS ⇧⌘P) and enter the command
Azure Functions: Deploy to Function App..., press Enter, and then select the function app name from the list.
- Open the Command Palette (For Windows Ctrl+Shift+P and macOS ⇧⌘P) and enter the command
- Testing the Deployed function App With Auth Keys
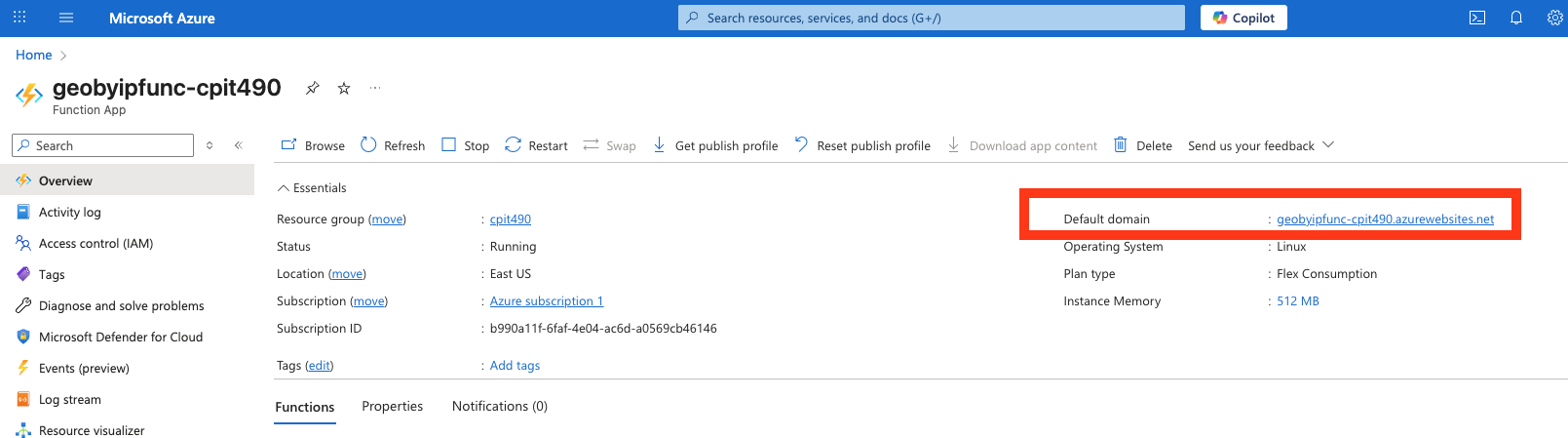
- Copy the domain of the function app from the Azure Portal.
- Testing the deployed function requires authentication keys. This is because in
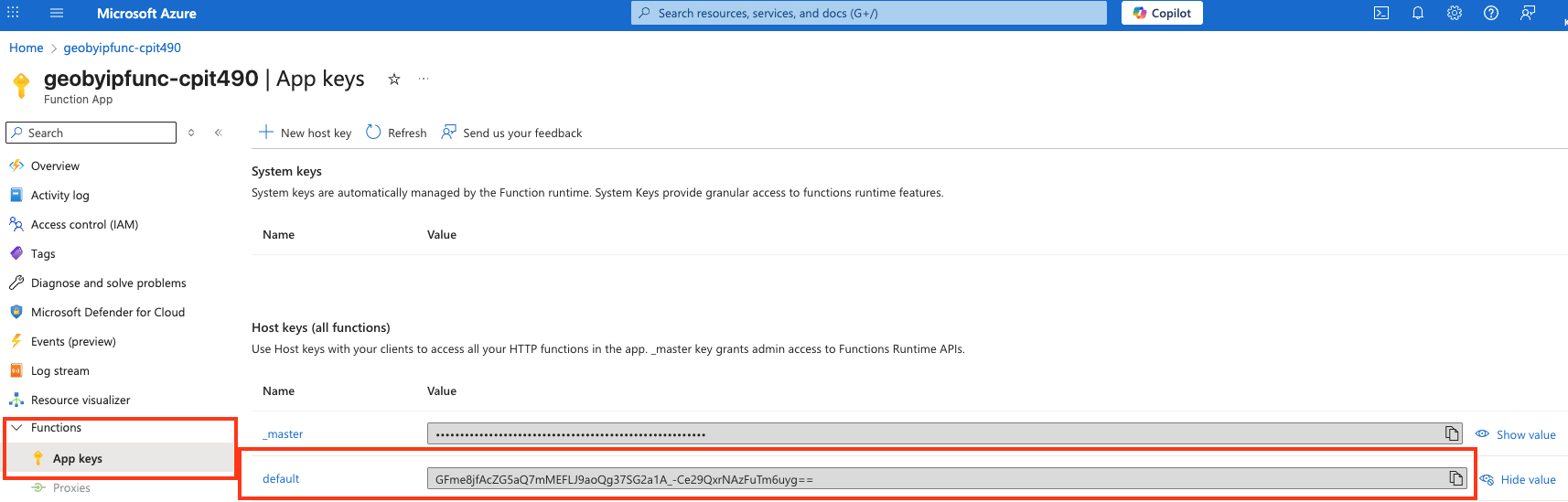
Function.java, we setauthLevel = AuthorizationLevel.FUNCTION, which will make the authorization level of our function anAuthLevel.FUNCTION, which means you need to include a function key in your request. Otherwise, the function will return HTTP status code 401, Unauthorized. We can obtain the function auth keys from the Azure portal under or using the Azure CLI.- Option 1: Azure Portal: Go to Functions -> App Keys -> Copy the default key:
- Option 2: Azure CLI: Run the following command after replacing the function app name and resource group name with your own:
az functionapp keys list --name geobyipfunc-cpit490 --resource-group cpit490{ "functionKeys": { "default": "GFme8jfAcZG5aQ7mMEFLJ9aoQg37SG2a1A_-Ce29QxrNAzFuTm6uyg==" }, "masterKey": "abcdefghijkldsmnopqrswvn7hb4Y4jT65zXJ99DAzFuun8tWA==", "systemKeys": {} } - Copy the auth key (functionKeys.default) and include it as a query parameter as follows:
curl "https://<AZURE_FUNCTION_DEFAULT_DOMAIN>?code=<FUNCTION_AUTH_KEY>&ip=<IPv4_ADDRESS>" - Option 1: Azure Portal: Go to Functions -> App Keys -> Copy the default key:
- For example:
curl "https://geobyipfunc-cpit490.azurewebsites.net/api/getLocation?code=GFme8jfAcZG5aQ7mMEFLJ9aoQg37SG2a1A_-Ce29QxrNAzFuTm6uyg==&ip192.162.72.233"
- Testing with Postman
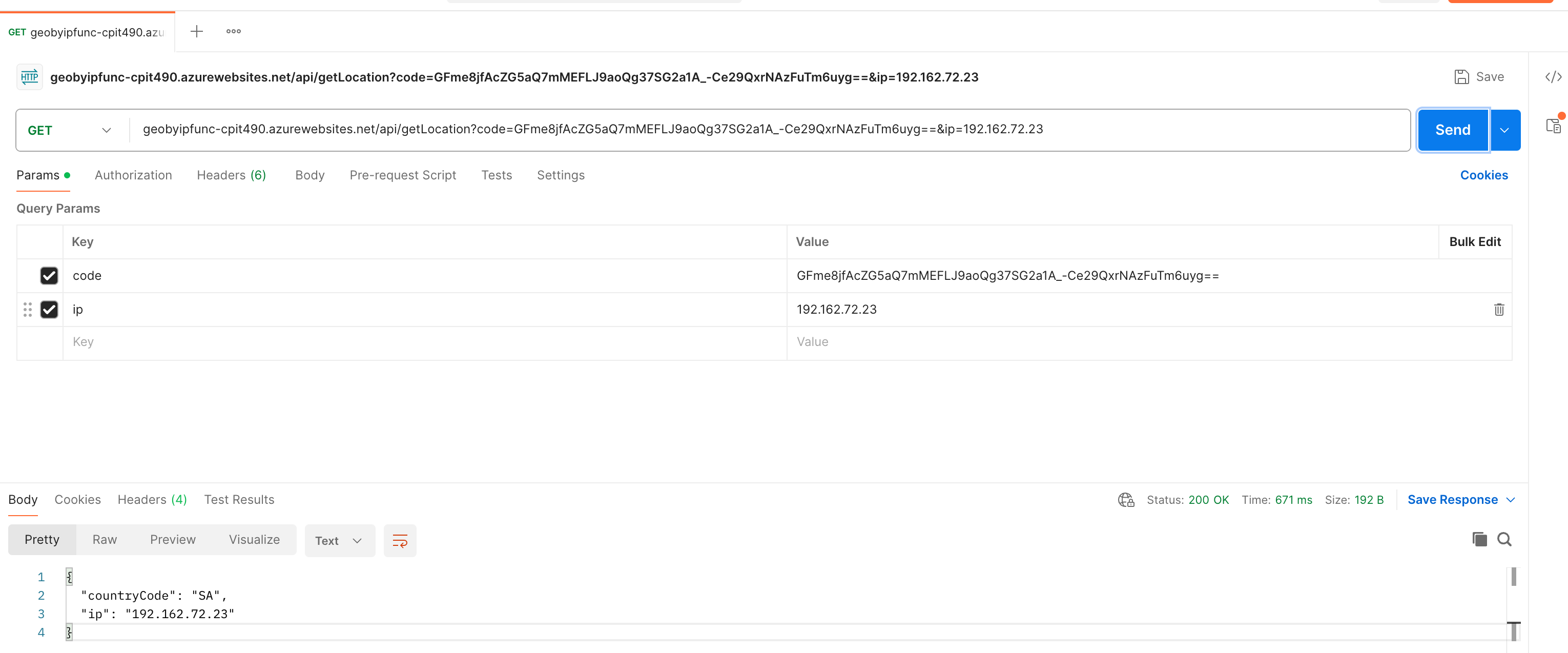
Open Postman and create a new GET request
Set the URL to your Azure Function endpoint with the auth key as a query parameter:
https://geobyipfunc-cpit490.azurewebsites.netUnder Query Params, add
- Key:
code - Value: The auth key (functionKeys.default) you obtained from the Azure portal or CLI as described in the previous step:
- Key:
ip - Value: Any IPv4 address (e.g.,
192.162.72.233)
- Key:
Click Send to test the function.
You should receive a JSON response similar to:
{ "countryCode": "SA", "ip": "192.162.72.23" }Example Postman configuration:
- Tear Down
- Delete the Function App and any associated resources from the Azure Portal.